For the past 30 years humans have been getting most of the visuals of space through the Hubble telescope. This masterpiece of engineering was launched back in 1990.

It is a large and most versatile, renowned both as a vital research tool and a PR boon for astronomy. The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA’s great observatories.
Here are some images taken by the mighty Hubble.

Lagoon Nebula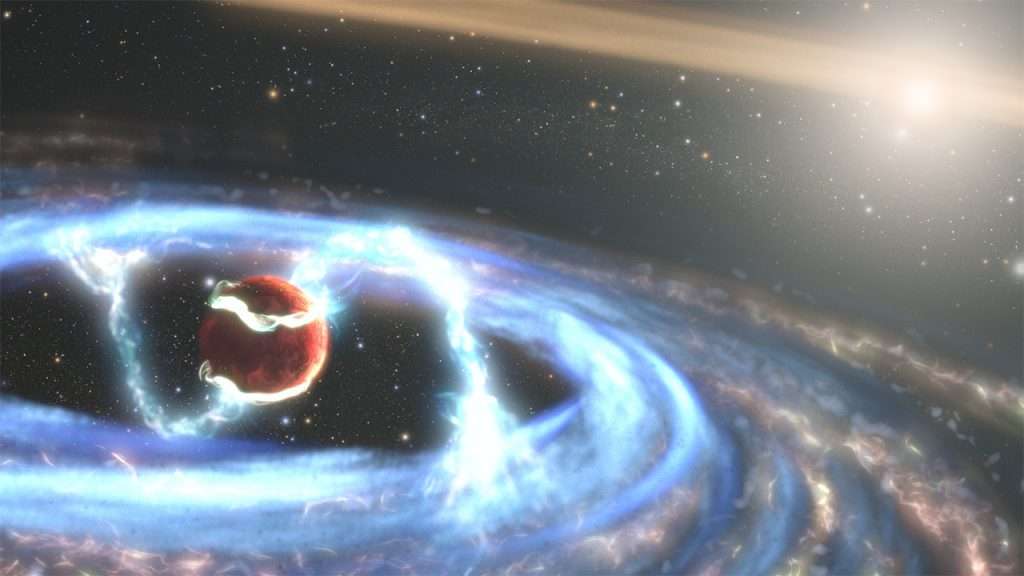 
PDS 70B Illustration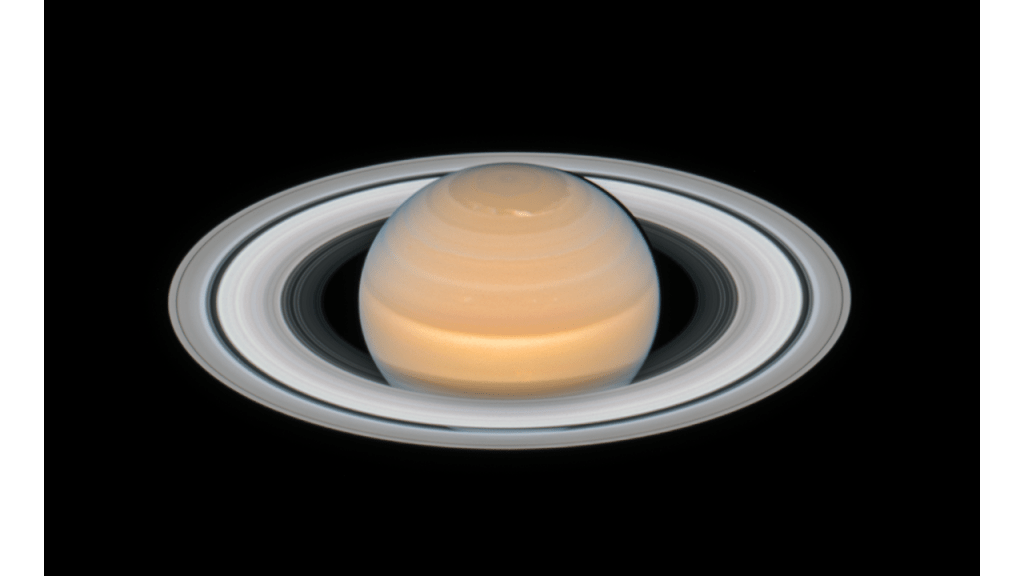 
Saturn 
Crab Nebula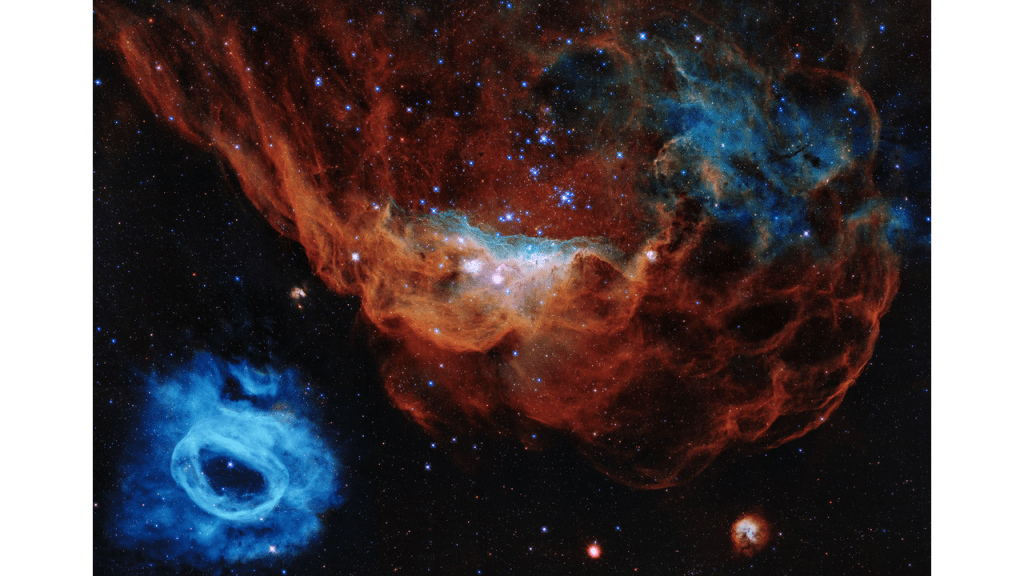 
Cosmic Reef 
Asteroids in Hubble Frontier
But as with most space projects there comes a time when they are decommissioned. They end up roaming around space with no proper trajectory or anyone that takes care of them.
The Hubble space telescope is set to be decommissioned somewhere between 2030 and 2040. We would obviously need a replacement for it to view our universe.
This is where the James Webb telescope comes in. It is planned to be a replacement for the hubble telescope. James Webb will be one of the greatest space projects in history.

The James Webb telescope has been in development since 1996. It was initially scheduled for launch in 2007 with a 500 million dollar budget. But this budget gradually became a 10 billion dollar expense and even the launch time has been excessively delayed.
After it was completed in 2016 it’s extensive testing began and it was set to launch in 2018. It was delayed twice in 2018 and once in march of 2020. JWST is now scheduled for launch on the 31st of October 2021.
So why is The James Webb space telescope so important to us?
Well that is because it can see 13 billion years into the past and observe the formation of the very first galaxies and planets that formed approximately 100 million years after the big bang, it may also be able to discover alien life for the first time ever.
But how is it able to do all that?
Here’s how.
Well first of all it will keep its mirror at a temperature of minus 388 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 233 degrees Celsius). The cold and the telescope’s distance from the Earth will give The James Webb the precision to observe red-shifted light from the early universe. The James Webb Space Telescope will detect infrared light that is 400 times fainter than what current space-based telescopes can see.
The telescope’s segmented primary mirror is 21 feet (6.4 m) in diameter and consists of 18 hexagonal segments made from gold-plated beryllium. A secondary mirror reflects light from the primary mirror into the science instruments to help produce an image.
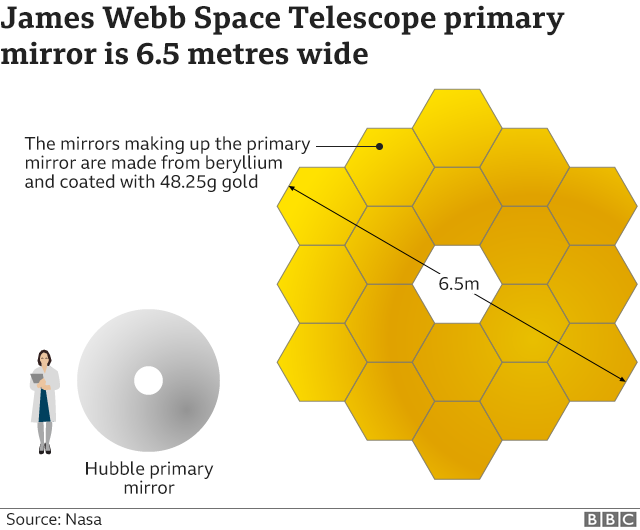
The James Webb’s mirror dwarfs that of the Hubble Space Telescope, but has one-tenth the mass of the Hubble’s mirror. Each of the 18 beryllium mirror segments weighs 46 pounds (20 kilograms).
But how will we look into the past?
That is just simple physics.
Human eye can only see objects when the light reflected from those objects reaches it. Light takes a lot of time to travel through space to reach Earth. We see events like supernovas thousands of years after they have actually occurred. Hence the huge mirror is used to reflect the infrared and cosmic radiations into the secondary mirror. It further transmits them to the instruments that will produce the image.
Because the mirror is so huge it needs to be folded as it is transported in Ariane 5 spacecraft.

Here is a video of the mirror folding:
The James Webb will travel for roughly 30 days to reach the orbital point. Orbital point is a gravitationally stable point about four times further from Earth than the moon. It will orbit around the Sun unlike the Hubble which orbits around the Earth. Unlike Hubble, Webb has not been designed to be serviced after launch. Astronauts will not visit it to repair and upgrade systems, as they did five times with the veteran space observatory.
“If we get to the point where we’re starting to run out of fuel, they might be able to mount a mission to go out and refuel The James Webb to keep it going”. NASA project manager Bill Ochs once told reporters.
The $10bn James Webb Space Telescope is a joint venture between the US, European and Canadian space agencies. Therefore is also a huge accomplishment in the engineering and space world.

Artist: JOANNA BARNUM (Image Credits: Flicker and NASA)
This telescope will be in service for about 10 years but it could be longer than that. It will also be able to answer questions that are unanswered for decades. It will will provide humans with a different and more clearer perspective of our universe.
![]()

16 years old, Studying in O levels, I have a passion for cars and am also very intrigued by engineering and space exploration. I plan to contribute to either of these fields in the future