Not all micro-organisms are bad. Some may be the opposite. “Probiotics” are the live microorganisms that are beneficial for human beings. The antiviral and immune strengthening effects of probiotics have been already proven by scientists.
Covid-19 is declared as a global pandemic by WHO. No matter how strictly the SOPs are followed, to fully get rid of the disease we need to come up with other ways to prevent and treat it. Covid-19 disease, a respiratory inflammatory disease, is different from SARS and there are not much existing medicines that worked for flu or other antiviral diseases and are effective against it. A person affected by COVID can be asymptomatic and PR symptomatic. This is why its ignored easily which leads to further worsening of the situation.
On cellular level the markers which play an important role are immunomodulatory markers such as proinflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, Interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-7, IL-12, interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4, IL-10, IL-11, and IL-13.
Now we have to see how probiotics play a role in combating this infection. Actually, probiotics are non-pathogenic, and their role have been seen in managing immune responses specially in viral infections through decades and have been proven through clinical trials. Studies have showed that if we take probiotic supplementation along with meat fiber it prevents us from viral infections. This leads to lower viral loads in the lungs and enhances survival rates.
Probiotics act as antiviral agents. The human respiratory tract is open to various viral viruses that cause infection and are deadly but human body also contains natural beneficial flora which traps these viral agents and fights against them. The most important probiotic strains are genera of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium which have been proven clinically to work against Respiratory syncytial virus and Influenza A virus (IFV).
Covid-19 spreads by human respiratory droplets. Upon entry in cells, it binds with type-2 alveolar epithelial cells. These epithelial cells are present in lungs, gastrointestinal tract, and kidneys and they serve as a reservoir for virus proliferation and replication. Human lungs have larger surface area, and they are covered with type-2 alveolar epithelial cells. This is the reason the disease manifest in them, and they are more vulnerable to the disease. As disease progresses, it causes cell damage by unbalancing the redox homeostasis.
Covid-19 patients have increased levels of proinflammatory cytokines TNFα, IFNγ, IL-2, IL-6, IL-7 leading to other abnormalities such as renal injury, myocardial injury, immune deficiency etc. This disease also leads to gut microbiota dysbiosis leading to nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. This infection is detected in esophagus, stomach, intestines, rectum, feces and in severe conditions lead to loss of gut barrier integrity and even in some cases death.
How do probiotics prevents Covid-19?
The best preventive strategy against an infection like COVID is to somehow enhance the host’s immunity. This can be easily and effectively achieved by probiotics.
According to a study, probiotics strain L. rhamnosus CRL1505, L. gasseri SBT2055, L. casei DK128, B. bifidum, and B. subtilis have shown to improve host immunity in mice models and also in human trials. These strains appear to be promising against covid-19 infection as they induce pro-inflammatory response and reduce upper respiratory tract infections and antibiotic associated diarrhea by approximately 70%. The cytokine storm which appears in covid-19 patients is mitigated by these probiotics strains and it does so by balancing cellular and humoral immune responses and redox homeostasis.
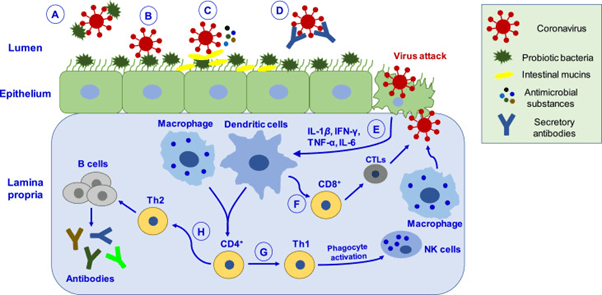
The proposed mechanism of probiotics is that when corona virus attacks the epithelial membranes, these probiotic bacteria release certain bacteriocins, lactic acid, biosurfactants, hydrogen peroxide, organic acids and nitric acids which stops virus proliferation. In this way, it modulates the host immune responses, balance Th1/Th2-mediated immunity, certain cytokines, and antibodies. Upon activation of immune response, CD8+ T-lymphocytes differentiates into cytotoxic T-lymphocytes and destroy cells which are infected by the corona virus. Moreover, activation of macrophages and phagocytosis by NK cells promotes killing of pathogens. Differentiation of CD4+ cells into Th2 cells induces B cells proliferation resulting in results in antibody production. These antibodies then combat coronavirus proliferation.
This is how probiotics can help manage COVID by balancing the redox homeostasis that is important to control the disease progression.
![]()